Papaverine for ED: a Surprisingly Cheap Drug that Compares to Viagra
What is Papaverine
Papaverine is a widely used drug belonging to a group of opium alkaloids, though its pharmacological action differs from such analgesic opium alkaloids as morphine or codeine. It has vasodilating, spasmolytic/antispasmodic and hypotensive effects. This makes it helpful in treating conditions involving spasm of smooth muscle.
The drug was discovered in 1848 by a German student, who later founded a well-known chemical and pharmaceutical company. It can be obtained from opium or prepared synthetically.
Pharmaceutical Forms
Papaverine may be available in various formulations, such as hydrochloride salt, adenylate, codecarboxylate, teprosylate. Adenylate and codecarboxylate are oral forms. Papaverine hydrochloride is intended for oral, rectal, intravenous and intramuscular administration; teprosylate – for oral, intravenous and intramuscular administration. Papaverine medications with different formulations are sold under different trade names.
Traditionally the medication is produced as:
- tabs for oral intake,
- solution for injections,
- rectal suppositories.
Auxiliary ingredients may vary depending on the manufacturers, who print the exact composition and amount of the ingredients in the medical instruction sheet.
Indications for Use
Papaverine is primarily used for relieving cramps, pain and discomfort that accompany different conditions and diseases. Thus, it’s prescribed for treating visceral spasm or colic, vasospasm (in particular, those involving brain, heart, ureter or the intestines), peripheral vascular disease, acute mesenteric ischemia, pulmonary and peripheral embolism, angina pectoris, subarachnoid hemorrhage. Muscle relaxing properties allow using it in microsurgery, which involves applying it directly to blood vessels. It’s also occasionally used in erectile dysfunction treatment – in the form of injections.
Off label use includes prophylaxis of migraine headaches, in situations when first line and secondary drugs fail to help or cause unwanted effects. Sometimes it’s prescribed in combinations with morphine, codeine, opium alkaloid salts and other drugs.
The drug reduces general muscle tone and relieves spasmodic pains of various intensity, thus restoring normal functioning of the organs. It has a complex effect on all systems and organs. It relaxes the smooth muscle, without affecting striated departments and without altering the contractility of skeletal and cardiac muscles. Thus, the agent relieves spasms and relaxes the organs’ muscles and blood vessels without adverse effects on the myocardial activity.
The drug softly lowers blood pressure and reduces excitability of the heart muscle. The use of high doses provides a sedative effect and stabilization of the central nervous system activity.
Full metabolization of the drug takes 24 hours.
Can Papaverine Be an Alternative to Viagra?
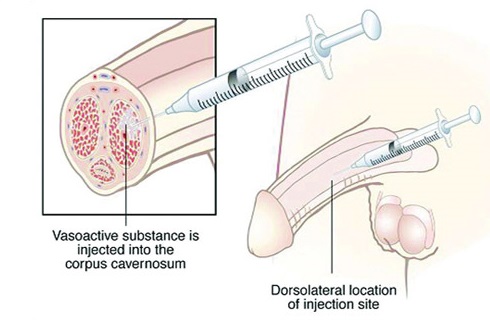
Penile tissue’s responses to sildenafil and papaverine are similar, but not the same. The medication is injected in penile tissues in order to relax smooth muscles and to make corpus cavernosum fill with blood, which results in better erection. The treatment often includes using a combination of drugs, when papaverine is injected together with phentolamine and prostaglandin. Any drug, a combination of drugs and their doses have to be approved by an urologist.
Papaverine’s mechanism of action is to some extent similar to that of Viagra, because it also inhibits a phosphodiesterase enzyme and causes elevation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels.
In some cases oral drugs fail to help men with erection and the doctor may prescribe injections. A medicine is introduced into the penis to make blood vessels expand. An increasing blood flow causes erection, even if there’ no sexual desire. And it is the difference between papaverine and sildenafil citrate – the latter one can’t provide erection if a man is not sexually aroused.
After the injection the following reactions are experienced:
- improved erection,
- increased sexual desire,
- stronger orgasm.
A vasoactive drug is injected in the base of the penis using a thin needle. An erection usually occurs within 15-20 minutes and lasts about an hour, while the cavernous bodies are filled with blood.
It may seem that papaverine is a better solution than Viagra, due to its fast action and effectiveness irrespective of presence of sexual desire. But it’s also a hazard because of the risk of complications such as priapism; this condition is characterized by abnormal erection lasting for more than 4 hours after the injection – it’s a serious side effect able to harm the penis.
Risks Associated with Injections Aimed at Improving Potency
If a man hadn’t have troubles with potency before, he should not use injections. If he has three or more sexual intercourses a week, it’s necessary to select another method of improving erection. This invasive method of restoring potency is not wide spread and is used only when all other options are exhausted.
In fact, regular penile injections are rather dangerous and may become a cause of the formation of fibroids and bruises. Sometimes after a long break, a man cannot achieve the desired erection; in this case, he may resort to injections to increase potency. Only a doctor must select the medicine for injections after full examination of the patient and identifying the underlying causes his problems. Self-treatment, incorrectly chosen medications or doses can lead to pathological processes.
The allowed frequency of injections is no more than once in 24 hours. Be cautious because frequent injections may lead to curvature of the penis, as a consequence of fibrosis of the corpora cavernosa.
Contraindications and Precautions
Injections for potency are usually prescribed in case of minimal risk of complications.

Papaverine should not be used in case of:
- hypersensitivity to papaverine,
- glaucoma,
- severe hepatic insufficiency,
- AV blockade,
- age under 6 or over 65.
Injections for ED treatment are contraindicated to men who have:
- diseases of heart and vessels,
- panic or nervousness,
- drugs/alcohol abuse,
- congenital anomalies and serious deformations of the penis,
- inflammation of cavernous bodies,
- peyronie’s disease,
- leukemia,
- sickle cell anemia,
- multiple myeloma,
Diabetic patients have risk of microhemorrhages with the further development of fibrosis of the penis, because of microangiopathy, so they should resort to other treatment methods.
Those who have bad eyesight or strong shaking of the hands should avoid such procedures so as not to hurt themselves.
To protect oneself from unpleasant consequences, it is advised to undergo therapy under the doctor’s supervision, and to read the instruction. The injection should be done properly. To avoid bruising, it is necessary to introduce the medicine on the opposite sides of the penis. It’s important when sexual acts occur every day.
To protect oneself and avoid problems, remember:
- not to exceed the prescribed dose,
- to abstain from drinking alcohol during the treatment and especially before injections,
- to stop smoking (it affects the effectiveness of the medicine),
- using the same syringe more than once is inadmissible.
Side Effects: Rare and Common Symptoms
Frequent papaverine adverse effects include:
- somnolence,
- vertigo,
- polymorphic ventricular tachycardia,
- constipation,
- increased levels of alkaline phosphatase or transaminase,
- interference with hepatic function test.
The following side effects happen not so often:
- headache,
- flushing of the face,
- tachycardia,
- excessive sweating,
- arterial hypotension,
- thrombopenia,
- jaundice,
- drug eruption,
- allergic reaction,
- chronic active or mixed hepatitis,
- eosinophilia,
- cerebral vasospasm aggravation,
- loss of appetite.
Penile injections are also able to cause hormonal misbalance, hypotension, mood swings, a decrease in the number and quality of sperm, swelling, pain in the injection area, formation of hard lumps in the injection area, entry of infection through the puncture.
The types of complications and probability of their development depends on the right dosage. A too high dose may cause priapism – a prolonged painful erection. Sometimes complications are accompanied by severe pain and deformation of the penis. In such situation only a doctor will help.
To minimize the risk of unwanted symptoms, don’t exceed the dosage prescribed by the doctor.