Canadian News: Immunofluorescence for iNOS
The expression of iNOS was significantly elevated in alveolar macrophages in BALF from the CA group. The expression of iNOS in polymorphonuclear cells in BALF was generally faint or negligible. Faint expression of iNOS was found in the L-NAME inhalation group. No expression of iNOS was found in the control group. 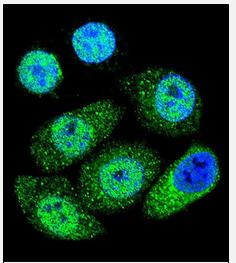
Paraffin-embedded sections from the CA group exhibited marked immunostaining after treatment with polyclonal antibody to iNOS. Immunoreactivity for iNOS was primarily found in alveolar epithelial cells. In the L-NAME inhalation group, however, immunostaining of iNOS was markedly attenuated, and only light staining of alveolar epithelial cells was observed. No significant immunoreactivity was detected in the control group.
In the CA group, immunohisto-chemical staining of protein nitrotyrosine residues was observed throughout the lung. The alveolar epithelial cells were darkly stained. After L-NAME inhalation, the alveolar epithelial cells were lightly stained. Scant staining was observed in lung tissue from the control group.
Twenty-four hours after C albicans injection there was marked inflammatory cell infiltration in the interstitium and airspaces of the lung in the CA group. Alveolar hemorrhage, fibrin deposition, and extravasated erythrocytes in the perivascular intersti-tium of arterioles were also observed. L-NAME inhalation markedly attenuated the alveolar exudate and lung injury. No inflammatory change was observed in the control group.
The serum TNF-a and IL-ip levels in the CA group were significantly higher than those in the control group. The serum IL-1p and TNF-a levels in the L-NAME inhalation group were significantly lower than those in the CA group.
By day 2 after infection, mortality was 60% in the CA group. No mortality was noted by day 2 after infection in the L-NAME inhalation group. Median survival was 1.3 days in the CA group and 3.2 days in the L-NAME inhalation group. This difference was statistically significant (p = 0.006 by the log-rank test). We could not determine the causes of death in our study, but survival was improved by treatment with inhaled L-NAME in mice with lethal candidemia.
Subscribe to our twitter and follow the news and promotions on our website: https://twitter.com/acanadianmall