Sublingual Melatonin: The Benefits Explained By Canadian Health&Care Mall
Melatonin is not available on the market only in the form of capsules or tablets. Preparations based on sublingual melatonin are also very common, but transdermal patches and oral sprays have also been developed.
Several studies have shown that 90% of the melatonin present in the blood is eliminated from the liver in the so-called ‘first pass’; consequently its half-life is very short (30-60 minutes). Clearly, the methods of administration influence the bioavailability of melatonin. For example, it has been calculated that on average only 33% of the ingested melatonin is absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract, with inter-individual variations ranging from 10% to 56%. In the case of sublingual administration, however, the amount of melatonin that reaches circulation may be 50% higher.
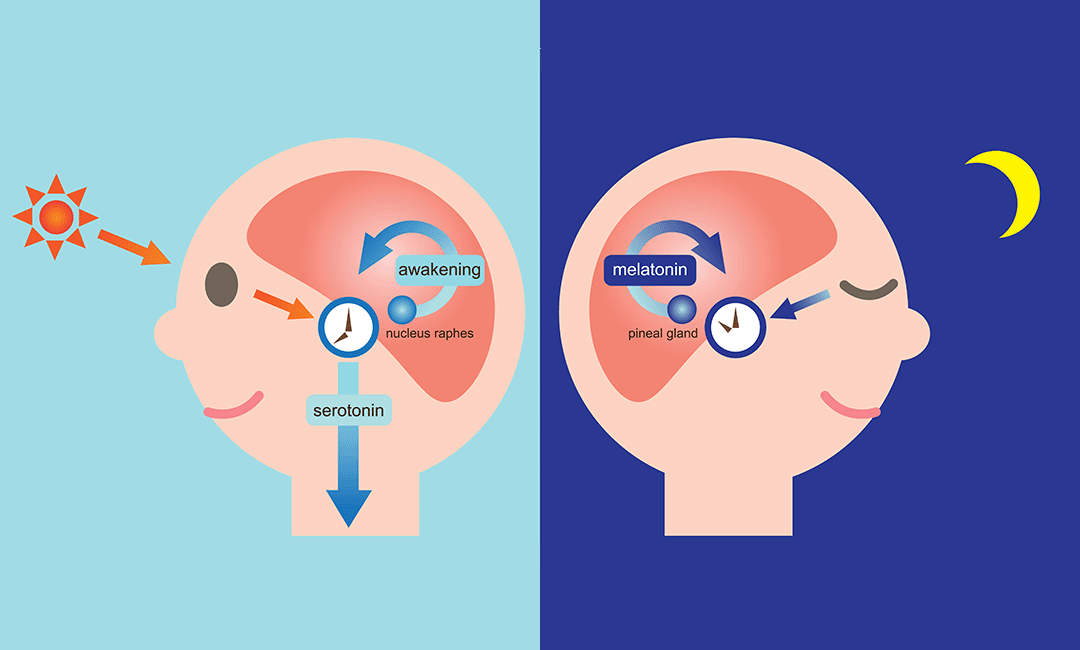
The possibility of bypassing the first pass metabolism, to which melatonin is very sensitive, means that the sublingually administered dose corresponds, in terms of bioavailability, to a double quota taken per os. Melatonin: directly derived from serotonin and even before tryptophan, is synthesized in a gland placed at the diencephalic level and known as epiphysis. The synthesis of this hormone is strongly regulated – in addition to the availability of the substrate – from the light / dark ratio. The light stimulus, in fact, received by cells similar to retinal photoceptors, activates a series of biological mechanisms that lead to total inhibition of the enzyme involved in melatonin synthesis.
It is therefore understood that the maximum production of this neurohormone is recorded at night, where the light stimulus is minimal. However, light is not the only stimulus capable of interfering with endogenous melatonin synthesis; in fact, even alcohol, smoking, tranquilizers, caffeine, vitamin B12, ibuprofen, other drugs and aging, greatly affect epiphyseal function. The integration with melatonin, in addition to the hypnotic and sedative effect, is able to protect the pineal gland, reducing its exhaustion and protecting it from calcification and degeneration.
The 5 benefits of sublingual melatonin can be therefore summed up as follows:
In addition to the regulation of the biological clock and the sleep / wake rhythm, its main application, melatonin also actively participates in other important reactions, such as:
- Oxidation-reduction reactions: the antioxidant function of melatonin and its metabolites is now known. The high level of protection offered by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, place it among the most important antioxidant molecules, despite the commitment in this process involves the net loss of the quota involved, given the absence of reductase able to regenerate it.
- Immune reactions: several experimental evidences have correlated the administration of melatonin to a significant strengthening of the immune defenses. More specifically, an improvement was observed in both the non-specific immune defenses (inflammatory reactions) and the adaptive defenses (improvement of the antibody and cytotoxic response).
- Protection reactions: melatonin is able to protect the cell, and in particular its DNA, from the action of mutagens. Although there are no valid trials on men, it was used in the cocktail of prof. Di Bella for her potential antitumor actions.
- Metabolic reactions: although still in the characterization phase, early evidence suggests that activation of the MT1 receptor for melatonin may improve insulin sensitivity and protect laboratory animals from the onset of type II diabetes.
- Sublingual absorption: sublingual absorption is an alternative route to classical oral administration and related gastric or intestinal absorption. Although the absorption surface is rather small (about 0.02 m2), the high vascularization of the sublingual region ensures an optimization of this process. The main advantages deriving from this method of administration are expressed in a faster kinetics, and above all in a greater bioavailability.
Despite the multiple capabilities of this molecule, currently melatonin is used in all those disorders and those conditions that involve difficulty in falling asleep and changes in the sleep / wake cycle.
Melatonin and physical activity: although there are no direct and particularly important benefits, related to the use of melatonin in sports practice, some studies highlight:
- Improvement of hormone secretion: in particular it seems that the administration of melatonin can optimize the secretion of GH in athletes undergoing resistance training;
- Antioxidant effect: together with other antioxidants, melatonin can guarantee greater protection of muscle tissue, and not only, from oxidative damage induced by intense physical activity;
- Enhancement of immune defenses: melatonin could be particularly useful to avoid the fall of the immune system, which follows intense training and characterizes the overtraining syndrome;
- No particular improvements have been made to the performance or body composition following melatonin intake.
Recommended use of sublingual melatonin: Canadian Health&Care Mall tips
Dissolve a plate under the tongue, before going to bed.

Given the pharmaceutical formulation proposed by the developing company, the only dosage that can be performed in this case is that of 3 milligrams / day, although in recent experimental evidences there have been registered overlapping effects as significantly inferior. In this case, moreover, it is necessary to consider the greater bioavailability of the product (which skips the first pass liver metabolism) and the more rapid absorption kinetics, which causes the plasma peak to be realized immediately after its administration, suggesting the use before bedtime for the night rest.
Several studies seem to agree on the greater effectiveness of the synergy when taken together with the zinc. A generalized improvement is obtained both on the strengthening of the immune defenses, on the antioxidant effect and on the metabolic aspect, improving the sensitivity to insulin. Some studies show that in case of prolonged intake of zinc and melatonin, the integration with magnesium. The validity of the simultaneous administration of melatonin and vitamin B6, is still under observation, even if the first works show an improvement in the endogenous synthesis of this hormone, with an enhancement of biological effects mainly related to the modulation of immune activity and hormonal.
Side effects of melatonin Canadian Health&Care Mall technicians warn against
While recent studies have confirmed the high tolerability and safety of the active ingredient, there are cases in the literature in which, even at the dose of 3 mg / day, nausea, irritability, nightmares and vascular alterations have been observed Also, acting as mild hypnotic and if dative, melatonin could interfere with the ability to concentrate. By enhancing the immune response, the substance may also worsen the conditions of patients suffering from allergic or autoimmune diseases.
The product is contraindicated in cases of renal or hepatic disease, cardiovascular disease and / or hypertension, allergies and autoimmune diseases, during pregnancy, during lactation, under the age of 12 and adolescents not yet trained. In case of prolonged use (over 6/8 weeks) the doctor’s opinion is necessary.