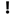20 Symptoms Of STDs You’d Better Be Able To Recognize Early
Unfortunately, STDs are a part of many modern people’s life. The risk to join the ranks of unlucky ones shouldn’t and cannot prevent people from having sexual life, but it should encourage them to take measures for protecting themselves. And it’s useful to know most common STD symptoms in order to be able to immediately respond the disease and timely receive the necessary treatment.
How One Can Get a Sexually Transmitted Infection
It’s important to understand that any type of sexual activity can be accompanies by transmission of infections – vaginal/anal/oral intercourses, genital touching.
You have to be sure that your partner doesn’t have a STI – this means to see the results of the medical tests. If you don’t know your partner well or for a long period of time, if you met him/her not so long ago and he/she looks healthy, this doesn’t guarantee he/she is not an infection carrier. In fact, STI or STD symptoms are not always noticeable, and a person can even be unaware of his/her infection/disease for a long time. Sometimes a person can also be a carrier without falling sick, but his/her partner falls sick soon after the sexual intercourse. And sometimes the STD symptoms can be mistaken for other conditions.
There’re no absolutely foolproof methods of protection against STI, though condoms are rather effective. So, it’s especially essential to be precautious and careful when having sexual contacts with new people. It’s much safer to have constant monogamous relationships or a marriage because when two initially healthy people have sex only with each other, they are not likely to bring infections from someone else.
Some diseases can only be transmitted through sex (gonorrhea), while for others it’s enough to get into contact with blood of an infected person (hepatitis).
Sometimes STI can be transmitted without sex at all – via reused syringes or some other ways, when an infection has an opportunity to get into blood, but such cases are rare and usually happen among drug addicts and in suchlike situations.
The Importance of STD Diagnostics and Timely Treatment
If you have sexual relationships with more than one constant (and faithful) partner you should regularly be tested for sexually transmitted infections, including asymptomatic ones. Untreated STIs involve many hazards, including complications and an increased risk of acquiring another STI (for example, HIV). This can happen because of the weakened immunity or formation of sores raising the risk of infections transmission. Infertility is one of the possible consequences of untreated STIs.
If you’ve discovered that you have a STI or a STD, inform your sexual partner so that he/she is able to receive timely medical help as well.
It’s easy to treat and cure some of the STIs, while in other situations more serious treatment is required.
Symptoms of Chlamydia
A wide-spread bacterial infection of a genital tract, Chlamydia is often asymptomatic and difficult to detect at the early stages. The signs of the disease are easy to overlook because they usually start 1-3 weeks after being exposed to an infection, and also because they are often mild.
Here are common Chlamydia symptoms:
- lower abdominal pain;
- pain during urination;
- abnormal discharge from the penis or from the vagina;
- pain in the testicles in men;
- bleeding between periods in women;
- painful sensations during sexual intercourse in women.
Symptoms of Trichomoniasis
Trichomonas vaginalis usually infects a man’s urinary tract without causing any symptoms and a woman’s vagina with symptoms appearing within 5-28 days, either mild or severe:
 inflammation in the genital area;
inflammation in the genital area;- pain during urination;
- painful sex;
- vaginal/penile irritation/itching;
- discharge from the penis;
- vaginal discharge (yellowish/greenish, white or clear);
- strong odor from the vagina.
Symptoms of Gonorrhea
After exposure to Gonorrhea infection the bacteria can grow in the eyes, mouth/throat and anus.
The symptoms can be noticed within 10 days, but in some people it takes several months:
- painful urination (or burning sensation during this process);
- bloody or thick vaginal/penile discharge;
- itching in the anus;
- painful bowel movements;
- swollen or painful testicles;
- bleeding between periods in women;
- heavy menstrual bleeding.
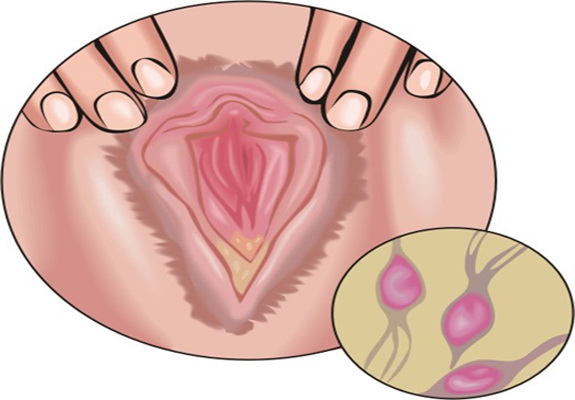
Symptoms of Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
There’re forms of HPV that cause genital warts in both sexes, the others are considered to increase the risk of cervical cancer in women. The Human Papillomavirus infection has no noticeable signs.
The symptoms appear when it develops into genital warts and include:
- discomfort/itching in the genital area;
- small swellings in the genital area;
- several warts in one area joint into clusters;
- bleeding during or after sex.
The size of genital warts can be only 1 mm. If case if oral sex with an infected partner took place, the warts can occur in the throat or mouth. But often there’re no symptoms at all.
Symptoms of Genital Herpes
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is able to enter the body through damaged skin or mucous membranes. A lot of people have this virus in them without knowing it, since the symptoms are absent, mild and unnoticed, or mistaken for flu signs.
If the symptoms become noticeable, the first Herpes episode is usually the worst. Some people never have the second episode, while the others have recurrent ones for decades.
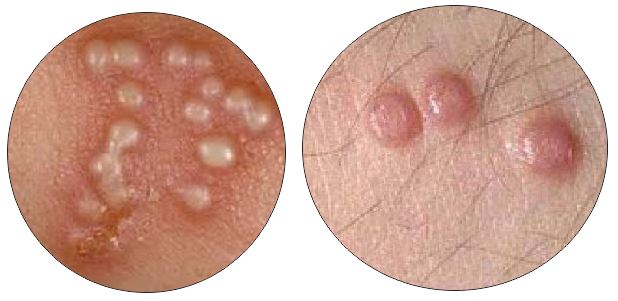 Genital herpes symptoms show like this:
Genital herpes symptoms show like this:
- headache;
- fever and muscle aches;
- swollen lymph nodes in the groin;
- painful urination;
- pain/itching in the genital area (appear within a few weeks after exposure);
- small red bumps (appear after several days);
- oozing or bleeding ulcers (open sores) in the genital/anal area.
Eventually, the ulcers heal and scabs form.
Symptoms of Hepatitis
Hepatitis A, B and C are infections of viral origin, of which the latter two are the most serious ones. The virus affects liver, causing inflammation.
In some people symptoms don’t develop.
But when they do, it usually happens after several weeks:
- yellowing of skin and eyes;
- dark urine;
- fatigue;
- loss of appetite;
- abdominal discomfort or pain, especially in the liver area;
- itching;
- muscle or joint pain;
- fever;
- nausea/vomiting.
Symptoms of Syphilis
This bacterial infection affects genitals, mucous membranes and skin. It can involve heart, brain and many other body parts. When an infected woman gets pregnant and the infection passes to her baby, this is called congenital syphilis and can be life-threatening to the infant.
There are several stages of development of syphilis symptoms:
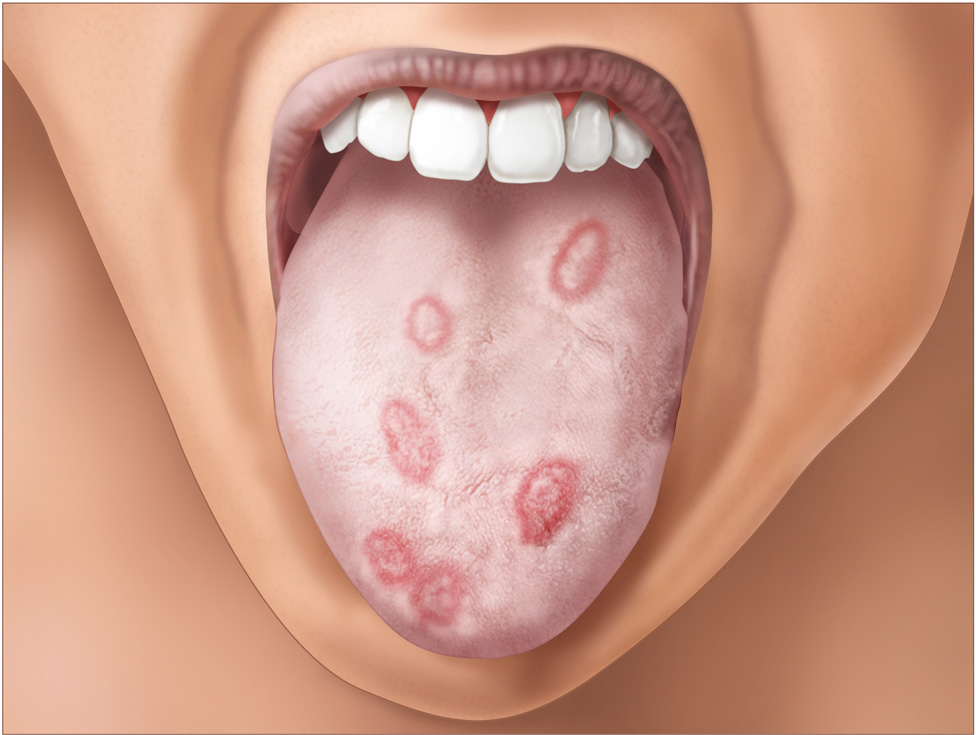
- Primary stage
The symptoms occur 10-90 days after exposure: small and painless chancres/sores (single or multiple) on the infected body part (lips, tongue, genitals, rectum). Though the sores usually heal without treatment, the uncured underlying disease may cause the next stages.
- Secondary stage
The symptoms of the second stage develop within 3-6 weeks after appearance of the chancres. They may disappear without treatment after a few weeks or return in the form of recurrent episodes during a year. There may occur: penny-sized sores of red/reddish-brown color on any area of the body, enlarged lymph nodes, fever, aching, discomfort and fatigue.
- Latent stage
This stage is characterized by absence of symptoms.
- Tertiary stage
The disease may progress to this stage or not. When syphilis bacteria spread as a result of lack of treatment, they damage internal organs and finally death follows after several years. The signs include numbness, lack of coordination, blindness, paralysis, and dementia.
- Neurosyphilis
Though the disease affects the nervous system at any stage, neurosyphilis may show itself in the form of headaches, movement problems and changes in behavior.
Symptoms of HIV
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) impairs the body’s ability to resist harmful fungi/bacteria/viruses. HIV infection can develop into AIDS – a severe life-threatening disease which is considered incurable at the moment.
The problem with HIV is that an infected person can have no symptoms for a long time and be unaware of his/her condition, while transmitting it to the sexual partners during unprotected sex. Some people have flu-like symptoms within up to 2 months. So HIV test is the only way to find out about being infected.
HIV may cause the following sings on the early stage:
- headache;
- fatigue;
- fever;
- rash;
- swollen lymph glands;
- sore throat.
The early symptoms tend to disappear within a week/month which allows people to mistake HIV infection for other viruses. More severe and persistent symptoms may show even in 10 years after the exposure to infection, while immune cells continue to be destroyed by the multiplying virus.
At this stage the signs of mild-to-moderate intensity may include:
- swollen lymph nodes;
- shortness of breath;
- coughing;
- fever;
- weight loss.
On the late stage the following symptoms of persistent and chronic character may appear:
- fatigue of unexplained origin;
- headaches;
- diarrhea;
- unusual/opportunistic infections;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- night sweating;
- fever or shaking chills for several weeks.
Summary: 20 Symptoms That May Point to a STD
As it can be seen from the information above, the majority of sexually transmitted diseases have similar symptoms that may include:
- fatigue;
- headaches;
- abdominal pain;
- painful sex;
- painful urination;
- abnormal discharges from the penis or from the vagina;
- inflammation in the genital area;
- itching in the genitals or anus;
- swollen or painful testicles;
- swollen lymph glands;
- bleeding between menstruations;
- rash;
- fever;
- sore throat;
- ache in the muscles;
- loss of appetite or weight;
- diarrhea;
- nausea/vomiting;
- sores/ulcers in the genital/anal area or other body parts;
- warts.
If any of these occurs to you and especially if you have the reason to suspect an infection, pay attention to your condition and visit a doctor/pass STI tests to exclude the possibility of infection. And if the infection is confirmed, don’t lose time and don’t delay the treatment. It is often rather easy to cure certain sexually transmitted diseases; in a range of cases a course of antibiotics is enough.